Differences between ADRs and regular stocks
What are American Depositary Receipts (ADRs)?
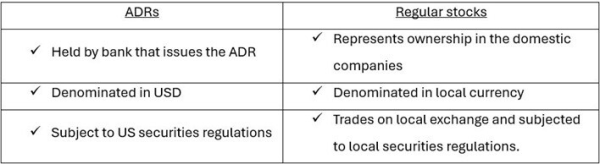
ADRs are financial instruments that represent ownership in shares of foreign companies. They are issued by US banks and trade on US exchanges. ADRs provide global investors with a convenient way to invest in foreign companies without the complications of trading on foreign exchanges.
Differences between ADRs vs Regular stocks
Advantages of ADRs vs Regular stock
- Diversification: ADRs enable investors to diversify their portfolio by gaining exposure to international markets which may not be available in the US. This reduces risk and potentially enhances returns by investing in foreign markets.
- Accessibility: ADRs offer investors an easy way to invest in foreign companies without the complexities of international investing including exchange rate fluctuations and transaction fees. This opens a wider range of opportunities beyond US stocks.
- Avoiding FX conversions: ADRs trade like regular stocks, making it convenient for investors to invest in US dollars without FX conversions. Dividends are also paid in US dollars, which simplifies the process of receiving dividend payments. But please note the implicit FX risk of investing in a company with non USD balance sheet in USD remains.
Disadvantages of ADRs vs Regular stock
- No voting rights: Regular stocks typically offer voting rights in company decisions while ADR holders are not necessarily entitled to the same rights.
- Liquidity: Regular stocks usually have better liquidity as they trade on the domestic exchange while ADRs could have lower liquidity which means you could be paying higher spreads to trade them.
- Costs: ADRs may have additional fees i.e. administrative and currency conversion costs. Administrative costs include charges from the Depository Trust Company in the US for holding ADRs and that can be in the range of 1-5 cents per share per year. Currency conversion costs exist because the ADR is priced in USD instead of the local currency.
- Company data: ADRs have differing regulatory requirements which could affect the levels of information investors can get their hands on. E.g. US uses GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) and Hongkong uses IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards)
- Trading hours: ADRs will be restricted to the trading hours of the US stock exchanges while regular stocks will follow the local stock exchange trading hours. Domestic investors who wish to trade during their daylight hours might prefer to buy domestic shares to facilitate management of their positions and orders.
Which is better?
Despite the advantages of ADRs, regular stocks may still be preferable for investors who look for the purest form of equity ownership, with currency exposure, voting rights and liquidity. Regular stocks have lesser fees compared to ADRs and they have a higher level of transparency. For those investors who are looking to build a well-diversified portfolio, direct regular stocks widen the universe of available stocks.
Ultimately, investors will need to weigh the advantages of both ADRs and regular stocks based on their strategies, risk appetite and investment objectives.
Introducing Saxo: Easy access to international markets
A leading investment platform like Saxo offers investors a wide range of investment opportunities, including stocks, ADRs, futures and leveraged instruments.
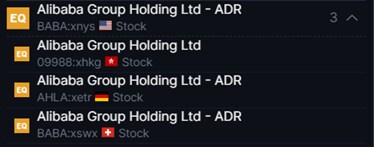
Saxo offers both the regular domestic stocks and ADRs which investors can leverage on to make better informed decisions that are aligned with their investment strategies and objectives. For example; we have Alibaba listed in Hong Kong as a regular domestic stock while also having its ADR listed in the US, Germany and Switzerland. The wide range of product options Saxo offers will ensure that investors will find something that suits their investment objectives.